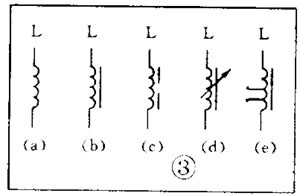
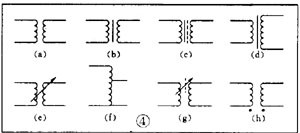
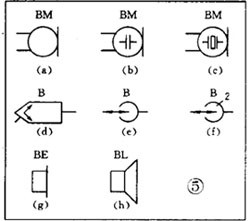
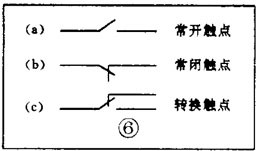
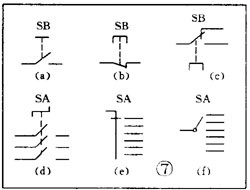
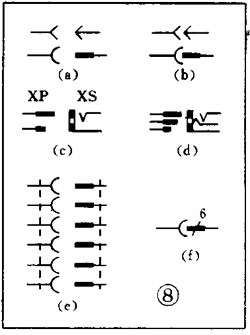
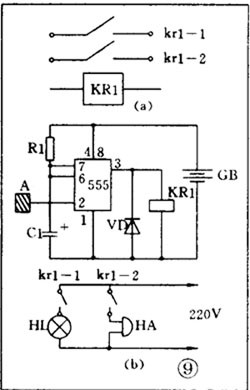
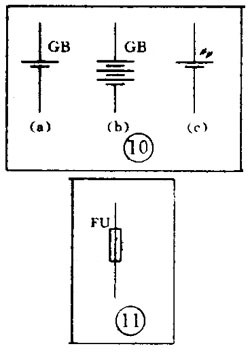
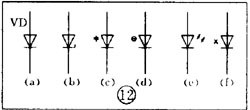
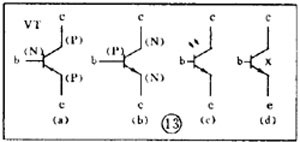
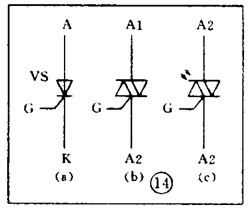
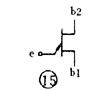
There are various kinds of pictures in electronic devices. It is the electrical schematic diagram, which is called the circuit diagram, which can explain how they work. There are two kinds of circuit diagrams, one is to explain the working principle of analog electronic circuits. It uses various graphical symbols to represent resistors, capacitors, switches, transistors, etc., and uses wires to connect components and unit circuits in accordance with the working principle. This type of picture has long been called a circuit diagram. The other is to explain the working principle of digital electronic circuits. It uses various graphical symbols to represent gates, flip-flops, and various logic components, and uses logical lines to connect them logically. It is used to illustrate the logical relationship between each logical unit and the logic function of the whole machine. In order to distinguish it from the circuit diagram of the analog circuit, the diagram is called a logic circuit diagram, referred to as a logic diagram. In addition to these two figures, there are commonly used block diagrams. It uses a box to represent a part of the circuit, which succinctly explains the relationship between the various parts of the circuit and the working principle of the whole machine. A circuit diagram is like an article. Various unit circuits are like sentences, and various components are words that make up sentences. So if you want to understand the circuit diagram, you have to start by knowing the word - the component. The contents, types, and methods of use of components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, and transistors have been introduced in the near future, so they will not be repeated in the lecture. This article only repeats the various symbols that often appear in the circuit diagram, I hope that beginners are familiar with them and remember not to forget. Resistor and potentiometer The symbol is shown in Figure 1, where (a) represents a general resistance fixed resistor, (b) represents a semi-adjustable or trimming resistor; (c) represents a potentiometer; (d) represents a potentiometer with a switch . The word symbol of the resistor is “Râ€, and the potentiometer is “RPâ€, that is, after the R, a character “P†indicating that it has the adjustment function is added. In some circuits, the power of the resistor is required, and can be represented by the symbols shown in (e), (f), (g), and (h) of Fig. 1, respectively. The symbols of several special resistors, the first is the thermistor symbol, and the resistance value of the thermistor varies with the outside temperature. Some are negative temperature coefficients, expressed by NTC; some are positive temperature coefficients, expressed by PTC. Its symbol is shown in ( i ), with θ or t° to indicate temperature. Its text symbol is "RT". The second type is the photoresistor symbol, see Figure 1 (j), with two oblique arrows indicating light. Its text symbol is "RL". The third type is the symbol of the varistor. The varistor resistance varies with the voltage applied across the resistor. The symbol is shown in Figure 1 ( k ), with the character U representing the voltage. Its text symbol is "RV". These three resistors are actually semiconductor devices, but it is customary to treat them as resistors. The fourth special resistor symbol is a newly appearing fuse resistor that combines the function of a resistor and a fuse. When the temperature exceeds 500 ° C, the resistance layer is quickly peeled off and the circuit is cut off, which can protect the circuit. Its resistance value is very small, and it is currently used in color TVs. Its graphical symbol is shown in Figure 1 (1), and the text symbol is "RF". Capacitor symbol See Figure 2 for details, where (a) denotes a capacitor of fixed capacity, (b) denotes a polar capacitor, such as various electrolytic capacitors, and (c) denotes a variable capacitor of adjustable capacity. (d) denotes a trimmer capacitor and (e) denotes a double-connected variable capacitor. The character symbol of the capacitor is C. Inductor and transformer symbol The graphical symbols of the inductor coil in the circuit diagram are shown in Figure 3. Where (a) is the general symbol of the inductor, (b) is the coil with the core or core, (c) is the coil with the gap of the core, and (d) is the adjustable inductor with the adjustable core, ( e) is an inductor with multiple taps. The word symbol of the inductor is "L". The graphical symbol of the transformer is shown in Figure 4. Where (a) is an air core transformer, (b) is a core or core transformer, (c) is a core transformer with a shield between the windings, (d) is a secondary center tapped transformer, (e) is A variable-coupling transformer, (f) is an autotransformer, (g) is a transformer with an adjustable core, and a small dot in (h) is a mark of the polarity of the transformer. Symbols for microphones, pickups, and recording and playback heads The symbol of the microphone is shown in Figure 5 (a)(b)(c), where (a) is the graphical symbol of a general microphone, (b) is a condenser microphone, and (c) is a piezoelectric crystal The graphical symbol of the phone. The text symbol of the microphone is "BM". Pickups are commonly known as phonographs. Figure 5 (d) is the graphical symbol of the stereo cartridge, and its text symbol is "B". Figure 5 (e) is a graphical symbol of a mono recording and playback head. If it is stereo stereo, add a "2" to the symbol, see Figure (f). Speaker, earphone symbol Speakers and earphones are transducer elements that convert electrical signals into sound. The symbol of the headset is shown in Figure 5 (g). Its text symbol is "BE". The symbol of the speaker is shown in Figure 5 (h), and its text symbol is "BL". Symbol of wiring component In electronic circuits, it is often necessary to switch on, off or switch the circuit, in which case wiring components are used. There are two main types of wiring components: one is a switch; the other is a connector. jQuery112406034074850802977_1505358922034? (1) Symbol of the switch There is at least one moving contact and one stationary contact in the electromechanical switch. When we move, push or rotate the switch mechanism by hand, the movable contact and the static contact can be turned on or off to achieve the purpose of turning the circuit on or off. There are generally three types of moving contact and static contact: 1 moving (normally open) contact, the symbol is shown in Figure 6 (a); 2 moving (normally closed) contact, the symbol is Figure 6 (b); 3 Change (convert) contacts, the symbol is shown in Figure 6 (c). One of the simplest switches has only one set of contacts, while a complex switch has several sets of contacts. The graphical symbols of the switch in the circuit diagram are shown in Figure 7. Where (a) denotes a general manual switch; (b) denotes a push button switch with a break contact; (c) denotes a push-pull switch with a set of changeover contacts; The bottom of the point indicates the push-pull action; (d) indicates the rotary switch, the contact with 3 poles at the same time; (e) indicates the push-pull 1×6 band switch; (f) indicates the symbol of the rotary 1×6 band switch . The text symbol of the switch uses "S", the control switch, the band switch can use "SA", and the push button switch can use "SB". ??? ( 2 ) Connector symbol The graphical symbols of the connector are shown in Figure 8. Where (a) denotes a plug and a socket, (in two ways) the left side represents the socket and the right side represents the plug. (b) indicates a plug that has been inserted into the outlet. (c) indicates a 2-pole connector, also known as a 2-pin connector. (d) indicates a 3-pole connector, which is a commonly used 3-pin stereo headphone jack. (e) indicates a 6-pole connector. For simplification, it can also be represented by the figure (f), and the number 6 is marked above the symbol to indicate that it is 6 poles. The text symbol of the connector is X. For the sake of distinction, the plug can be indicated by "XP" and the socket by "XS". Relay symbol Since the relay is composed of two parts: the coil and the contact group, the graphical symbol of the relay in the circuit diagram also includes two parts: one long square indicates the coil; and one set of contact symbols indicates the contact combination. When the contactless circuit is relatively simple, the contact group is often drawn directly on one side of the coil frame. This drawing is called a concentrated representation, as shown in Figure 9 (a). When there are many contacts and the circuits controlled by each pair of contacts are different, a discrete representation is often used for convenience. That is, the coil is drawn in the control circuit, and the contacts are respectively drawn in the respective controlled circuits according to the respective working objects. This technique is advantageous for simplifying and analyzing circuits. However, this method must be marked with the number of the relay and the number of the contact at each pair of contacts, and stipulate that all contacts should be drawn in the original state in which the relay is not energized. Figure 9 (b) is a touch switch. When the human hand touches the metal piece A, the 555 time base circuit output (3 terminals) is high, so that the relay KR1 is energized, and the contact is closed to make the lamp light to make the electric bell sound. The 555 time base circuit is the control section and uses 6 volts low voltage. The lights and bells are controlled and use 220 volts. The text symbols of the relay are all "K". Sometimes for the sake of distinction, "KA" for AC relays, "KR" for electromagnetic relays and reed relays, and "KT" for time relays. Battery and fuse symbol The graphical symbol of the battery is shown in Figure 10. The long line indicates the positive pole, the short line indicates the negative pole, and sometimes the short line can be drawn thicker for emphasis. Figure 10 (b) shows a battery pack. Sometimes the battery pack can be simplified as a battery, but beside the voltage or the number of batteries. Figure 10 (c) is a graphical symbol of a photovoltaic cell. The battery symbol is "GB". The graphical symbol of the fuse is shown in Figure 11, and its text symbol is "FU". Diode, triode symbol The graphical symbols of the semiconductor diode in the circuit diagram are shown in Figure 12. Where (a) is the sign of a diode, the direction indicated by the arrow is the direction of current flow, that is, it is terminated on the diode and it is turned on when the lower terminal is connected to a negative voltage. Figure (b) is the Zener diode symbol. Figure (c) is the varactor symbol, and the capacitor symbol next to it indicates that its junction capacitance varies with the voltage across the diode. Figure (d) is the thermal diode symbol. Figure (e) shows the LED symbol, which is illuminated by two obliquely radiating arrows. Figure (f) is a magneto-sensitive diode symbol that responds to external magnetic fields and is often used as a proximity switch for automatic control. The word symbol of the diode is “Vâ€, sometimes it is different from the triode, and may also be represented by “VDâ€. Since the polarity requirements of the power supply are different when the PNP type and the NPN type transistor are used, they should be distinguishable and represented in the graphic symbol of the triode. The standard specification for graphic symbols: as long as it is a PNP type transistor, whether it is made of germanium or silicon, it is represented by Figure 13 (a). Similarly, as long as it is an NPN type transistor, whether it is made of germanium or silicon, it is represented by Figure 13 (b). Figure 13 (c) is the symbol of the phototransistor. Figure 13 (d) shows a silicon NPN type magnetic-sensitive triode. Thyristor, single junction transistor, FET symbol A thyristor is an abbreviation for a thyristor or a thyristor. Commonly used are unidirectional thyristors, triacs, and photo-controlled thyristors, and their symbols are (a)(b)(c) in Fig. 14, respectively. The text symbol for the thyristor is "VS". The symbol for a single junction transistor is shown in Figure 15. An electric field controlled semiconductor device, called a field effect transistor, has the symbol shown in Figure 16, where (a) represents an N-channel junction field effect transistor and (b) represents an N-channel enhancement type insulated gate field effect transistor. (c) denotes a P-channel depletion-type insulated gate field effect transistor. Their text symbols are also "VT". Feature: Surgery Goggles,Eye Safety Goggles,Best Safety Goggles,Eye Goggles Protection Guangzhou HangDeng Tech Co. Ltd , https://www.hangdengtech.com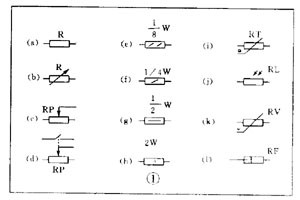

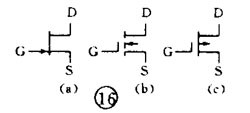
1.Material:The parts the wearer touches are not made of materials that can cause skin irritation
2.Structure:Smooth surface, no burr, no acute Angle and other defects that may cause eye and face discomfort.
It has good air permeability.
Adjustable parts and structural parts are easy to adjust and replace.
3.Package:The products are properly packaged and are accompanied by product certificates and instructions
4.fixing band : The minimum width of the headband in contact with the wearer is 11.5mm. The headband is adjustable, soft and durable
5.The appearance quality of the lens: the surface of the lens is smooth and free from scratches, ripples, bubbles, impurities, and other obvious defects that may impair vision
6.Diopter: 0.04D
7.The difference between the prism degrees of the left and right eye lenses: 0.12
8.Visible light transmission ratio: colorless transparent lens 89.35
9.Impact resistance: qualified
10.Protection performance of chemical fog drops: there is no color spot on the test paper within the center of the lens
11.Irritant gas protection performance: there is no color spot on the test paper within the center of the lens