PON technology originated from the ATMPON technology standard that began to take shape in 1995. PON is the abbreviation of "passive optical network" in English. GPON (Gigabit-Capable Passive Optical Network) was first proposed by the FSAN organization in September 2002. On this basis, ITU-T completed the formulation of ITU-T G.984.1 and G.984.2 in March 2003. The standardization of G.984.3 was completed in February and June. Thus finally formed the standard family of GPON. Gpon Olt,4 PON,8 PON,Gpon 16 Ports Olt,10G Port, GPON Device,Uplink Port Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com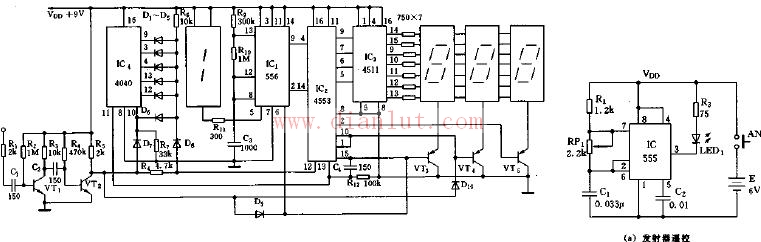
Radio digital frequency display circuit diagram
The basic structure of the equipment based on GPON technology is similar to the existing PON. It is also composed of OLT (optical line terminal) at the central office and ONT/ONU (optical network terminal or called optical network unit) at the user side. Optical fiber (SM fiber) and passive splitter (Splitter) composed of ODN (optical distribution network) and network management system.
The technical feature of GPON is that it borrows the GFP (Generic Framing Procedure) technology defined by ITU-T at the second layer, expands support for GEM (General Encapsulation Methods) encapsulation format, and reorganizes services of any type and any rate. It is transmitted by PON, and the GFM frame header contains frame length indicator bytes, which can be used for the transmission of variable-length data packets, which improves the transmission efficiency, so it can support all services more simply, universally and efficiently.
555 integrated radio digital frequency display circuit
The 555 circuit, which contains two voltage comparators, a basic RS flip-flop, and a discharge switch T, the comparator's reference voltage is provided by a voltage divider consisting of three 5K resistors. They respectively make the non-inverting input of the high-level comparator A1 and the inverting of the low-level comparator A2, and the reference levels of the input terminals are 2/3VCC and 1/3VCC. The outputs of the A2 and A2 control the RS flip-flop state and Discharge tube switch status. When the input signal is from the 6 pin, that is, the high level triggers the input and exceeds the reference level 2/3VCC, the flip-flop resets, the output of the 555 pin 3 outputs a low level, and the discharge switch tube is turned on; when the input signal is from 2 The input of the pin is lower than 1/3VCC, the trigger is reset, the 3 pin of 555 outputs high level, and the discharge switch tube is cut off. RD is the reset terminal (4 pins). When RD=0, 555 outputs a low level. Usually the RD end is open or connected to VCC.