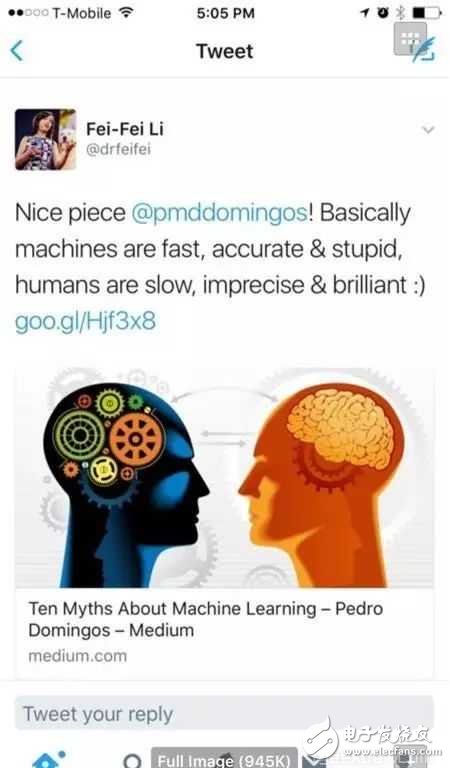
For many learners who are new to artificial intelligence, the concepts and differences between artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning are not well understood. It is possible that you can hear this concept every day and often mention this concept, but you Really understand the relationship between them? Then let's elaborate on the concept and characteristics. First look at the relationship between the three. Artificial intelligence includes machine learning, machine learning includes deep learning, and they are the relationship between subclasses and parent classes. The picture below is more subdivided. Artificial intelligence (ArTIficial Intelligence), abbreviated as AI. It is a branch of computer science. It has been called one of the world's three cutting-edge technologies (space technology, energy technology, artificial intelligence) since the 1970s. It is also considered to be one of the three cutting-edge technologies (genetic engineering, nanoscience, artificial intelligence) in the 21st century. In the summer of 1956, a group of forward-looking young scientists, led by McCarthy, Minsky, Rochester and Shennong, gathered together to study and discuss a series of related problems with machine simulation intelligence, and proposed for the first time. The term "artificial intelligence" marks the official birth of the emerging discipline of "artificial intelligence." Artificial intelligence is a simulation of the information process of human consciousness and thinking. Artificial intelligence is not human intelligence, but it can be like human thinking, and it may exceed human intelligence. Mathematics is often regarded as the basic science of many disciplines. Mathematics also enters the field of language and thinking. Artificial intelligence disciplines must also borrow mathematical tools. Practical application of artificial intelligence: machine vision, fingerprint recognition, face recognition, retina recognition, iris recognition, palmprint recognition, expert system, automatic planning, intelligent search, theorem proof, game, automatic programming, intelligent control, robotics, language And image understanding, genetic programming, etc. It involves philosophical and cognitive science, mathematics, neurophysiology, psychology, computer science, information theory, cybernetics, and uncertainty. Research areas include natural language processing, knowledge representation, intelligent search, reasoning, planning, machine learning, knowledge acquisition, combined scheduling problems, perception problems, pattern recognition, logic programming soft computing, inaccurate and uncertain management, artificial life, Neural networks, complex systems, genetic algorithms, etc. Artificial intelligence is currently divided into: strong artificial intelligence (BOTTOM-UP AI) and weak artificial intelligence (TOP-DOWN AI). If you are interested, you can check the difference yourself. Machine Learning (ML) is the core of artificial intelligence. It belongs to a branch of artificial intelligence. It is a large field. It is to let computers have the same learning ability as human beings, to simulate and realize human learning behaviors and abilities. The ability to recognize and judge like a human can be seen as bionics. The core of machine learning is data, algorithms (models), and computational power (computer computing power). There used to be artificial intelligence and machine learning. However, in recent years, network development and the accumulation of big data have enabled artificial intelligence to play its role in data and high computing power. Machine learning applications are extensive, such as: data mining, data classification, computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), biometrics, search engines, medical diagnostics, detecting credit card fraud, securities market analysis, DNA sequencing, speech and handwriting. Identification, strategy games and robotics. Li Feifei said that the machine is fast and accurate, but human beings are smart! Machine learning is actually summarizing data and predicting unknowns. It has high-speed computing power, we can continue to learn to use it to identify a variety of plants, animals, etc., and improve accuracy. Machine learning is to design an algorithm model to process the data and output the results we want. We can continuously adjust the algorithm model to form more accurate data processing capabilities. But this kind of learning will not make the machine conscious. How machine learning works 1. Select data: Divide your data into three groups: training data, validation data, and test data. 2. Model data: Use training data to build models that use related features. 3. Verify the model: Use your verification data to access your model. 4. Test model: Use your test data to check the performance of the validated model. 5. Use the model: Use a fully trained model to make predictions on new data. 6. Tuning the model: Use more data, different features, or adjusted parameters to improve the performance of the algorithm. Classification based on learning strategies 1. Mechanical learning (Rote learning) 2. Learning from instrucTIon or Learning by being told 3. Deduction Learning (Learning by deducTIon) 4. Learning by analogy 5. Explana-based learning (EBL) 6. Induction learning (Learning from induction) Classification based on representation of acquired knowledge Algebraic expression parameter Decision tree 3. Formal grammar 4. Production rules 5. Formal logical expressions 6. Diagram and network 7. Framework and schema 8. Computer programs and other process codes 9. Neural network 10. Combination of multiple representations Comprehensive classification 1. empirical inductive learning 2. Analytic learning 3. Analogy learning 4. Genetic algorithm 5. Join learning 6. Reinforcement learning Learning form classification 1. supervised learning 2. Unsupervised learning Note: There are semi-supervised learning and reinforcement learning in the subdivision. Of course, the latter deep learning also has the distinction of supervised learning, semi-supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Energy 8000,Energy Vape Pen,Energy 8000 Disposable,Energy 8000 Puff Disposable Vape Shenzhen Zpal Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zpal-vape.com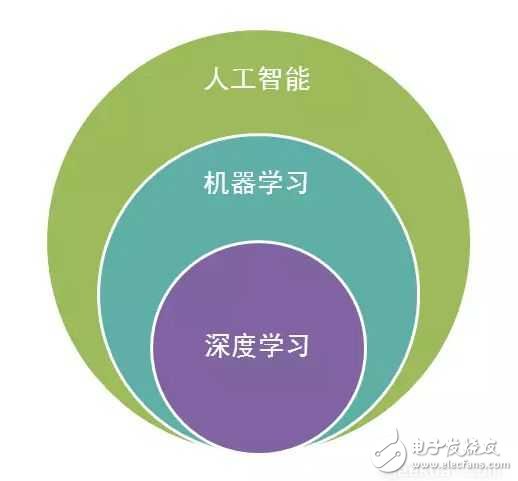
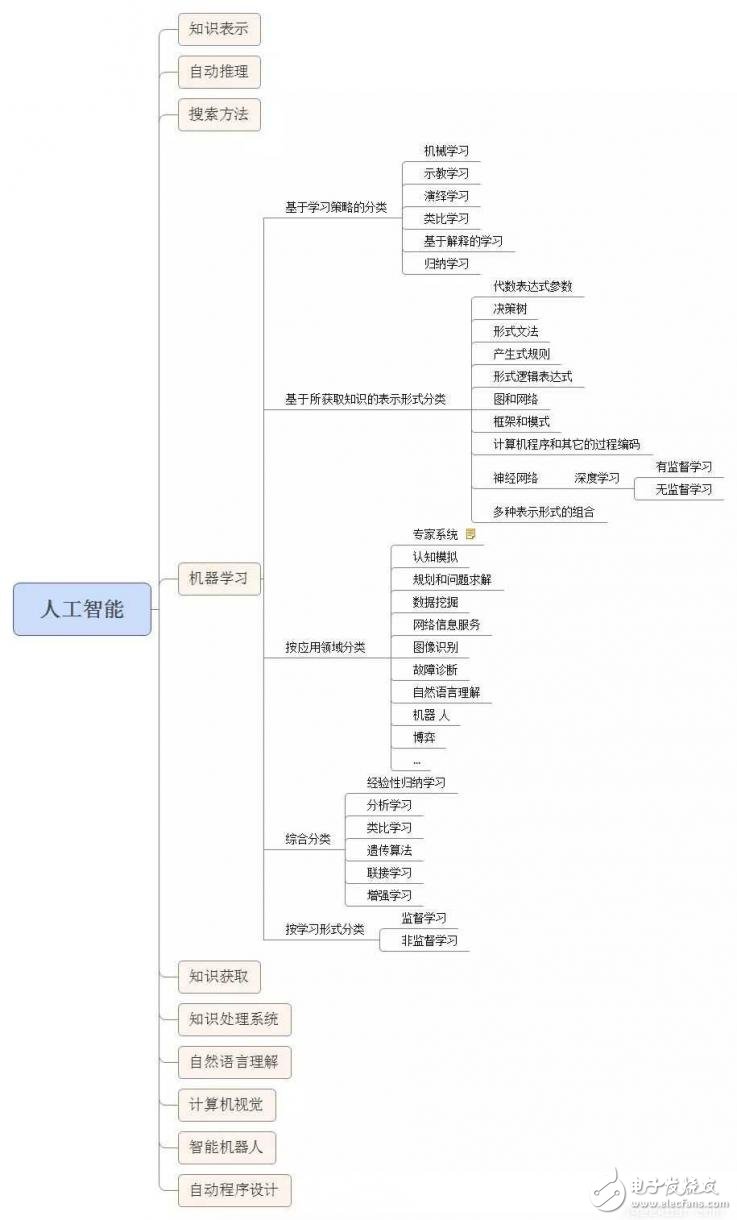

Analysis of the relationship between artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning
1. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning